Today, we’re diving into the fascinating world of AI agents with a handy guide I like to call the “ABC of AI Agents.” Think of this as your alphabet book for understanding the building blocks of these clever digital helpers. Just as learning the alphabet helps you read a story, mastering these terms will help you grasp how AI agents work their magic. So, grab a cuppa, and let’s get started!
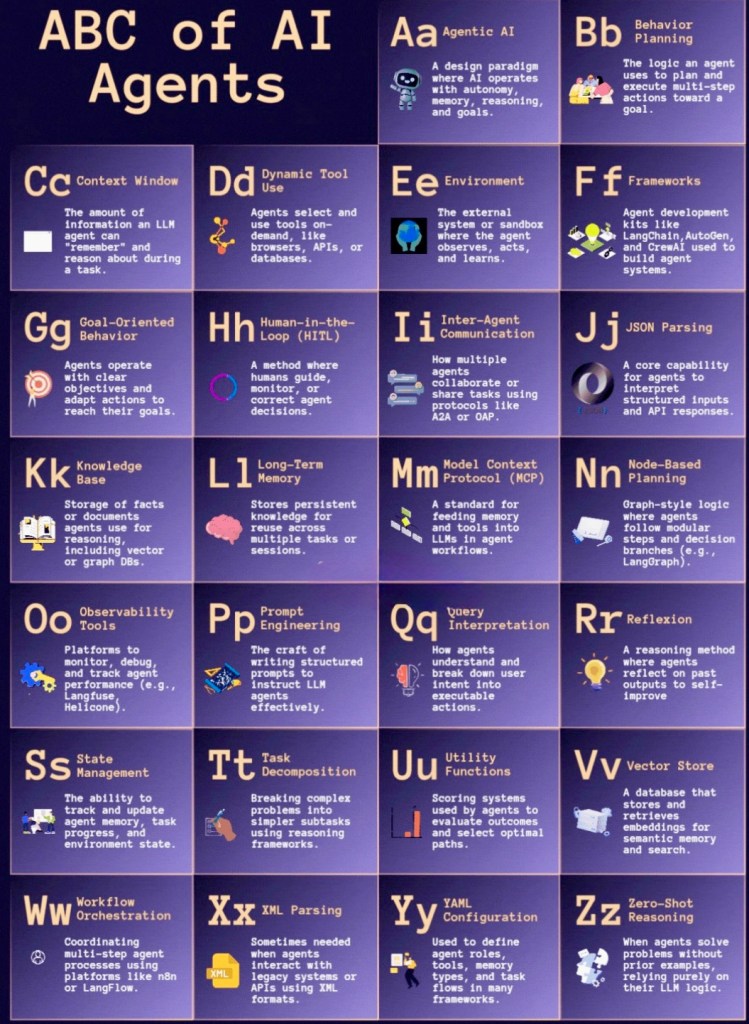
Aa – Agentic AI: The Brainy Helper
Imagine an AI agent as a trusty personal assistant, like a super-smart butler from a classic British novel. Agentic AI is all about giving this assistant some independence—think of it as teaching them to make a cup of tea without you holding their hand. They use memory, reasoning, and goals to get the job done.
Bb – Planning
Planning is like plotting a route for a Sunday drive through the countryside. This is where the AI agent figures out the best multi-step journey to reach its goal, whether that’s solving a problem or completing a task.
Cc – Context Window: The Memory Frame
Picture a context window as the size of a photo frame on your mantelpiece. It holds just the right amount of information an AI can “see” and think about while working, like remembering the recipe while baking a cake.
Dd – Dynamic Tool Use: The Swiss Army Knife
Dynamic tool use is like giving your AI a Swiss Army knife. It can pick the perfect tool—be it a browser, API, or database—to tackle the task at hand, adapting as needed.

Ee – Environment: The Playground
The environment is the playground where the AI agent romps around. It’s the external world or sandbox where the agent watches, learns, and interacts, much like kids exploring a park.
Ff – Frameworks: The Building Kits
Frameworks are like Lego sets for AI development. Tools like LangChain or AutoGen are the instruction manuals that help build these agent systems step by step.
Gg – Goal-Oriented Behaviour: The Target Practice
Think of goal-oriented behaviour as archery practice. The AI agent aims at clear targets (goals) and adjusts its shots (actions) to hit the bullseye.
Hh – Human-in-the-Loop (HITL): The Co-Pilot
HITL is like having a co-pilot in your car. A human monitors or guides the AI, stepping in to correct the course when needed, ensuring a smooth ride.
Ii – Inter-Agent Communication: The Team Chat
This is the office watercooler chat for AI agents. They collaborate on tasks using protocols like A2A or OAP, sharing ideas to get the job done.
Jj – JSON Parsing: The Language Decoder
JSON parsing is like a translator for the AI. It decodes structured inputs from APIs into something the agent can understand and act upon.
Kk – Knowledge Base: The Library
A knowledge base is the agent’s personal library, stuffed with facts and documents. It’s used for reasoning, like flipping through a cookbook for the perfect recipe.
Ll – Long-Term Memory: The Scrapbook
Long-term memory is like a family scrapbook. It stores persistent knowledge across tasks or sessions, so the AI remembers past adventures.
Mm – Model Context Protocol (MCP): The Toolbox
MCP is the toolbox that feeds tools and workflows into the AI, standardising how it operates, much like a carpenter’s kit for building furniture.
Nn – Node-Based Planning: The Roadmap
Node-based planning is like following a treasure map with branching paths (e.g., LangGraph). The AI plots its course through a graph-style logic.
Oo – Observability: The Dashboard
Observability is the car dashboard for AI. Platforms monitor, debug, and track performance (like Helicone), keeping the agent running smoothly.
Pp – Prompt Engineering: The Recipe Writing
Prompt engineering is like writing a recipe for your AI chef. It crafts structured instructions to guide the language model effectively.
Qq – Query Interpretation: The Mind Reader
Query interpretation is like a mind reader at a party. The AI understands and breaks down user intent to execute the right actions.
Rr – Reflection: The Self-Review
Reflection is like a personal review after a project. The AI looks back at past actions to improve its future performance.
Ss – State Management: The Memory Keeper
State management is like a diary for the AI. It tracks and updates the agent’s memory and environment state as it progresses.
Tt – Task Decomposition: The Puzzle Solver
Task decomposition is like breaking a jigsaw puzzle into smaller pieces. The AI splits complex tasks into simpler subtasks for easier solving.
Uu – Utility Functions: The Decision Maker
Utility functions are like a sat-nav choosing the best route. They help the AI evaluate outcomes and pick optimal paths.
Vv – Vector Store: The Memory Bank
A vector store is like a memory bank with embedded treasures. It retrieves data for semantic search, aiding the AI’s reasoning.
Ww – Workflow Orchestration: The Conductor
Workflow orchestration is like a conductor leading an orchestra. It coordinates multi-step processes using platforms like n8n or LangFlow.
Xx – XML Parsing: The Old-School Translator
XML parsing is like an old-school translator. It’s sometimes needed to interact with legacy systems or APIs using XML formats.
Yy – YAML Configuration: The Blueprint
YAML configuration is the blueprint for a house. It defines agent roles, memory, tools, and task flows in many frameworks.
Zz – Zero-Shot Reasoning: The Quick Thinker
Zero-shot reasoning is like solving a riddle without prior examples. The AI relies on its logic to figure things out on the fly.
There you have it—the ABC of AI agents, explained with a bit of British flair and everyday analogies! Whether you’re a curious newbie or a budding techie, this guide should give you a solid starting point. Fancy diving deeper? Let me know, and I can search for more details if needed. Cheers!


Leave a comment