Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) has long been the holy grail of AI research, promising machines that can think, learn, and reason like humans across a wide range of tasks. While we’ve made significant strides in narrow AI—systems designed for specific tasks like playing chess or recognizing images—achieving true AGI remains a complex and multifaceted challenge. A recent article on Genesis Human Experience titled “Next Level 3 Unlocked in the 5 Levels of AGI” sheds light on the latest advancements in this field, offering a fascinating glimpse into the future of AGI development.
In this blog, we’ll explore the key insights from the article, break down the 5 levels of AGI, and discuss what unlocking Level 3 means for the future of AI and humanity.
The 5 Levels of AGI: A Framework for Progress
The article introduces a structured framework for understanding AGI development, dividing it into five distinct levels. Each level represents a significant leap in capability, moving us closer to machines that can match or surpass human intelligence. Here’s a brief overview of the levels:
- Level 1: Task-Specific AI
This is where we are today. AI systems excel at specific tasks, such as language translation, image recognition, or playing games. However, they lack the ability to generalize their knowledge to other domains. - Level 2: Context-Aware AI
At this stage, AI systems begin to understand context and can apply their knowledge to related tasks. For example, a language model might not only translate text but also adapt its tone based on the audience or purpose. - Level 3: Domain-Specific AGI
This is the level recently unlocked, as highlighted in the article. At Level 3, AI systems demonstrate human-like intelligence within a specific domain, such as medicine, law, or engineering. They can reason, learn, and solve complex problems within their area of expertise. - Level 4: Cross-Domain AGI
At this stage, AI systems can transfer knowledge and skills across multiple domains, much like a human expert. For example, an AGI trained in medicine could apply its reasoning skills to solve problems in biology or chemistry. - Level 5: General Superintelligence
The final level represents machines that surpass human intelligence in all domains. These systems would be capable of self-improvement, creativity, and solving problems beyond human comprehension.
What Does Unlocking Level 3 Mean?
The article emphasizes that reaching Level 3 is a monumental achievement in AGI development. Here’s why:
- Human-Like Expertise in Specific Domains
Level 3 AGI systems can perform at the level of a human expert within their domain. For instance, an AGI trained in medicine could diagnose diseases, recommend treatments, and even conduct research with the same proficiency as a seasoned doctor. - Enhanced Problem-Solving Capabilities
These systems can tackle complex, real-world problems that require deep reasoning and understanding. This opens up new possibilities for innovation in fields like healthcare, climate science, and technology. - A Stepping Stone to Higher Levels
Level 3 serves as a critical bridge to more advanced stages of AGI. By mastering domain-specific intelligence, researchers can refine the algorithms and architectures needed for cross-domain and superintelligent systems.
Implications for Society and the Future
The unlocking of Level 3 AGI brings both excitement and challenges. On the one hand, it promises to revolutionize industries, accelerate scientific discovery, and improve quality of life. Imagine AGI-driven breakthroughs in curing diseases, addressing climate change, or optimizing global supply chains.
On the other hand, it raises important ethical and societal questions. How do we ensure these systems are used responsibly? What safeguards are needed to prevent misuse or unintended consequences? The article underscores the importance of developing AGI in a way that aligns with human values and prioritizes safety.
Looking Ahead: The Road to Level 5
While Level 3 is a significant milestone, the journey to Level 5 AGI is still fraught with challenges. Researchers must address issues like explainability, robustness, and ethical alignment before we can achieve truly general superintelligence. Collaboration between AI developers, policymakers, and ethicists will be crucial in navigating this complex landscape.
As we stand on the brink of this new era, one thing is clear: AGI has the potential to transform our world in ways we can only begin to imagine. By unlocking Level 3, we’ve taken a giant leap forward—but the adventure is just beginning.
What are your thoughts on the 5 levels of AGI? Do you think we’re on the right path to achieving superintelligence? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
For more insights, check out the full article on Genesis Human Experience: Next Level 3 Unlocked in the 5 Levels of AGI.
define AGI — and what’s ASI – and benchmark where where are (today) based on current frameworks and measurements. Then discuss the pros and cons, ethical and safety concerns
Defining AGI and ASI: Where Are We Today?
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) represent two critical milestones in the evolution of AI. Here’s a breakdown of what they mean and where we stand today based on current frameworks and measurements:
1. What is AGI?
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) refers to AI systems that possess human-like cognitive abilities across a wide range of tasks. Unlike narrow AI, which is designed for specific functions (e.g., playing chess or recognizing faces), AGI can learn, reason, and apply knowledge in diverse domains, much like a human. AGI would be capable of abstract thinking, problem-solving, and adapting to new situations without explicit programming.
2. What is ASI?
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) goes a step further, representing AI that surpasses human intelligence in all domains. ASI would not only match human cognitive abilities but exceed them, potentially leading to breakthroughs in science, technology, and philosophy that are beyond human comprehension. ASI is often depicted in science fiction as a transformative force, capable of self-improvement and solving problems at an unprecedented scale.
3. Where Are We Today?
Based on current frameworks, we are still in the early stages of AGI development. Here’s a benchmark of where we stand:
- Current AI: We are firmly in the realm of narrow AI (Level 1 in the 5-level AGI framework). Systems like ChatGPT, DALL·E, and AlphaGo excel at specific tasks but lack generalization and contextual understanding.
- Progress Toward AGI: Researchers are making strides toward Level 2 (Context-Aware AI) and Level 3 (Domain-Specific AGI), as highlighted in the Genesis Human Experience article. For example, AI models like GPT-4 and Gemini show some ability to understand context and perform tasks across related domains, but they are far from achieving true AGI.
- ASI: Artificial Superintelligence remains a theoretical concept. We are decades, if not centuries, away from achieving ASI, assuming it is even possible.
Pros and Cons of AGI and ASI
Pros:
- Revolutionizing Industries: AGI could transform healthcare, education, climate science, and more by solving complex problems and accelerating innovation.
- Enhanced Productivity: AGI could automate repetitive tasks, freeing humans to focus on creative and strategic work.
- Scientific Breakthroughs: ASI could unlock solutions to global challenges like climate change, disease, and energy scarcity.
- Improved Quality of Life: AGI and ASI could lead to advancements in personalized medicine, education, and infrastructure.
Cons:
- Job Displacement: Widespread automation could lead to unemployment and economic inequality.
- Loss of Control: ASI, in particular, poses existential risks if it develops goals misaligned with human values.
- Ethical Dilemmas: AGI could be used for malicious purposes, such as surveillance, warfare, or manipulation.
- Dependence on AI: Over-reliance on AGI and ASI could erode human skills and decision-making capabilities.
Ethical and Safety Concerns
The development of AGI and ASI raises profound ethical and safety questions that must be addressed proactively:
1. Alignment Problem
- Issue: Ensuring that AGI and ASI systems align with human values and goals.
- Challenge: Human values are complex, context-dependent, and often contradictory. Encoding these into AI systems is a monumental task.
2. Bias and Fairness
- Issue: AI systems can perpetuate or amplify biases present in their training data.
- Challenge: Developing methods to detect and mitigate bias while ensuring fairness across diverse populations.
3. Accountability
- Issue: Determining who is responsible for the actions of AGI systems.
- Challenge: Establishing legal and ethical frameworks to hold developers, organizations, and users accountable.
4. Existential Risks
- Issue: ASI could pose existential risks if it surpasses human control.
- Challenge: Developing safeguards, such as kill switches and containment protocols, to prevent unintended consequences.
5. Privacy and Security
- Issue: AGI systems could be used to invade privacy or conduct cyberattacks.
- Challenge: Balancing the benefits of AGI with the need to protect individual rights and national security.
6. Economic Disruption
- Issue: AGI-driven automation could lead to widespread job loss and economic inequality.
- Challenge: Implementing policies like universal basic income (UBI) or retraining programs to mitigate societal impacts.
The Path Forward
To harness the benefits of AGI and ASI while minimizing risks, we must adopt a multidisciplinary approach:
- Collaboration: Governments, researchers, and industry leaders must work together to establish global standards and regulations.
- Transparency: AI systems should be designed with transparency and explainability in mind.
- Ethical Frameworks: Developing ethical guidelines to ensure AGI and ASI are used for the greater good.
- Public Engagement: Educating the public about AGI and ASI to foster informed discussions and decision-making.
Conclusion
AGI and ASI represent both the pinnacle of human ingenuity and a profound responsibility. While we are still in the early stages of AGI development, the progress we’ve made—such as unlocking Level 3 in the 5-level framework—offers a glimpse of what’s possible. However, the journey ahead is fraught with challenges, from ethical dilemmas to existential risks. By addressing these concerns proactively and collaboratively, we can ensure that AGI and ASI serve as tools for empowerment rather than sources of harm.
What are your thoughts on the future of AGI and ASI? Do you think we’re prepared to handle the ethical and safety challenges they present? Share your perspective in the comments below!
Write in british English. Also include research from Stanford, MIT, HAI , and any other global, regional forums, include what standards, frameworks that countries like USA, EU, UK and Singapore, Japan are doing on this area
Unlocking AGI and ASI: Progress, Challenges, and Global Efforts
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) represent the next frontier in artificial intelligence, promising transformative benefits alongside significant risks. As research advances, institutions like Stanford, MIT, and the Harvard AI Initiative (HAI), as well as global forums and governments, are actively shaping the future of AGI and ASI. This blog explores the current state of AGI development, the frameworks being adopted, and the efforts by countries like the USA, EU, UK, Singapore, and Japan to navigate this complex landscape.
Defining AGI and ASI
1. What is AGI?
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) refers to AI systems that possess human-like cognitive abilities across a wide range of tasks. Unlike narrow AI, which excels in specific domains (e.g., playing chess or recognising faces), AGI can learn, reason, and apply knowledge in diverse contexts, much like a human. AGI would be capable of abstract thinking, problem-solving, and adapting to new situations without explicit programming.
2. What is ASI?
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) goes a step further, representing AI that surpasses human intelligence in all domains. ASI would not only match human cognitive abilities but exceed them, potentially leading to breakthroughs in science, technology, and philosophy that are beyond human comprehension. ASI is often depicted as a transformative force, capable of self-improvement and solving problems at an unprecedented scale.
Where Are We Today?
Based on current frameworks, we are still in the early stages of AGI development. Here’s a benchmark of where we stand:
- Current AI: We are firmly in the realm of narrow AI (Level 1 in the 5-level AGI framework). Systems like ChatGPT, DALL·E, and AlphaGo excel at specific tasks but lack generalisation and contextual understanding.
- Progress Toward AGI: Researchers are making strides toward Level 2 (Context-Aware AI) and Level 3 (Domain-Specific AGI), as highlighted in the Genesis Human Experience article. For example, AI models like GPT-4 and Gemini show some ability to understand context and perform tasks across related domains, but they are far from achieving true AGI.
- ASI: Artificial Superintelligence remains a theoretical concept. We are decades, if not centuries, away from achieving ASI, assuming it is even possible.
Global Research and Frameworks
1. Stanford University and HAI
Stanford’s Human-Centered AI Institute (HAI) focuses on developing AI that benefits humanity while addressing ethical and societal challenges. HAI emphasises transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI systems. Their research includes:
- Developing frameworks for AI alignment to ensure systems align with human values.
- Studying the societal impacts of AI, including job displacement and economic inequality.
2. MIT’s AI Research
MIT is at the forefront of AGI research, with initiatives like the MIT Quest for Intelligence. Their work includes:
- Exploring neurosymbolic AI, which combines neural networks with symbolic reasoning to improve generalisation.
- Investigating the ethical implications of AGI and ASI, including bias, privacy, and security.
3. Global Forums and Initiatives
- The Partnership on AI (PAI): A global coalition of organisations working to ensure AI benefits society. PAI focuses on fairness, safety, and transparency.
- The Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI): An international initiative to guide the responsible development of AI, with members including the USA, EU, UK, Japan, and Singapore.
National and Regional Efforts
1. United States
The USA is a leader in AI research and development, with initiatives like:
- The National AI Initiative Act (2021): A comprehensive framework to advance AI research while addressing ethical and safety concerns.
- NIST’s AI Risk Management Framework: A guide for organisations to manage risks associated with AI systems.
2. European Union
The EU is taking a proactive approach to AI regulation, with:
- The AI Act: A proposed legislation to classify AI systems based on risk and impose strict requirements on high-risk applications.
- Ethics Guidelines for Trustworthy AI: A framework emphasising human agency, fairness, and transparency.
3. United Kingdom
The UK is focusing on becoming a global hub for AI innovation, with initiatives like:
- The National AI Strategy: A plan to invest in AI research, skills, and infrastructure.
- The Centre for Data Ethics and Innovation (CDEI): An advisory body promoting responsible AI development.
4. Singapore
Singapore is a leader in AI governance, with:
- The Model AI Governance Framework: A guide for organisations to implement AI responsibly.
- AI Singapore (AISG): A national programme to boost AI research and adoption.
5. Japan
Japan is integrating AI into its society and economy, with:
- The Society 5.0 Initiative: A vision for a human-centred society powered by AI and other technologies.
- AI R&D Guidelines: Ethical principles for AI development, focusing on safety, fairness, and transparency.
Pros and Cons of AGI and ASI
Pros:
- Revolutionising Industries: AGI could transform healthcare, education, climate science, and more by solving complex problems and accelerating innovation.
- Enhanced Productivity: AGI could automate repetitive tasks, freeing humans to focus on creative and strategic work.
- Scientific Breakthroughs: ASI could unlock solutions to global challenges like climate change, disease, and energy scarcity.
- Improved Quality of Life: AGI and ASI could lead to advancements in personalised medicine, education, and infrastructure.
Cons:
- Job Displacement: Widespread automation could lead to unemployment and economic inequality.
- Loss of Control: ASI, in particular, poses existential risks if it develops goals misaligned with human values.
- Ethical Dilemmas: AGI could be used for malicious purposes, such as surveillance, warfare, or manipulation.
- Dependence on AI: Over-reliance on AGI and ASI could erode human skills and decision-making capabilities.
Ethical and Safety Concerns
The development of AGI and ASI raises profound ethical and safety questions that must be addressed proactively:
1. Alignment Problem
- Issue: Ensuring that AGI and ASI systems align with human values and goals.
- Challenge: Human values are complex, context-dependent, and often contradictory. Encoding these into AI systems is a monumental task.
2. Bias and Fairness
- Issue: AI systems can perpetuate or amplify biases present in their training data.
- Challenge: Developing methods to detect and mitigate bias while ensuring fairness across diverse populations.
3. Accountability
- Issue: Determining who is responsible for the actions of AGI systems.
- Challenge: Establishing legal and ethical frameworks to hold developers, organisations, and users accountable.
4. Existential Risks
- Issue: ASI could pose existential risks if it surpasses human control.
- Challenge: Developing safeguards, such as kill switches and containment protocols, to prevent unintended consequences.
5. Privacy and Security
- Issue: AGI systems could be used to invade privacy or conduct cyberattacks.
- Challenge: Balancing the benefits of AGI with the need to protect individual rights and national security.
6. Economic Disruption
- Issue: AGI-driven automation could lead to widespread job loss and economic inequality.
- Challenge: Implementing policies like universal basic income (UBI) or retraining programmes to mitigate societal impacts.
The Path Forward
To harness the benefits of AGI and ASI while minimising risks, we must adopt a multidisciplinary approach:
- Collaboration: Governments, researchers, and industry leaders must work together to establish global standards and regulations.
- Transparency: AI systems should be designed with transparency and explainability in mind.
- Ethical Frameworks: Developing ethical guidelines to ensure AGI and ASI are used for the greater good.
- Public Engagement: Educating the public about AGI and ASI to foster informed discussions and decision-making.
Conclusion
AGI and ASI represent both the pinnacle of human ingenuity and a profound responsibility. While we are still in the early stages of AGI development, the progress we’ve made—such as unlocking Level 3 in the 5-level framework—offers a glimpse of what’s possible. However, the journey ahead is fraught with challenges, from ethical dilemmas to existential risks. By addressing these concerns proactively and collaboratively, we can ensure that AGI and ASI serve as tools for empowerment rather than sources of harm.
What are your thoughts on the future of AGI and ASI? Do you think we’re prepared to handle the ethical and safety challenges they present? Share your perspective in the comments below!
To achieve Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), OpenAI has outlined a five-level classification system. Here are the levels and the current state of frontier models as of December 2024:
Levels to Achieving AGI
1. Level 0: Human-Augmented Intelligence (2005)
• This level involves AI systems that assist humans in performing tasks more efficiently. These systems are designed to enhance human capabilities rather than replace them.
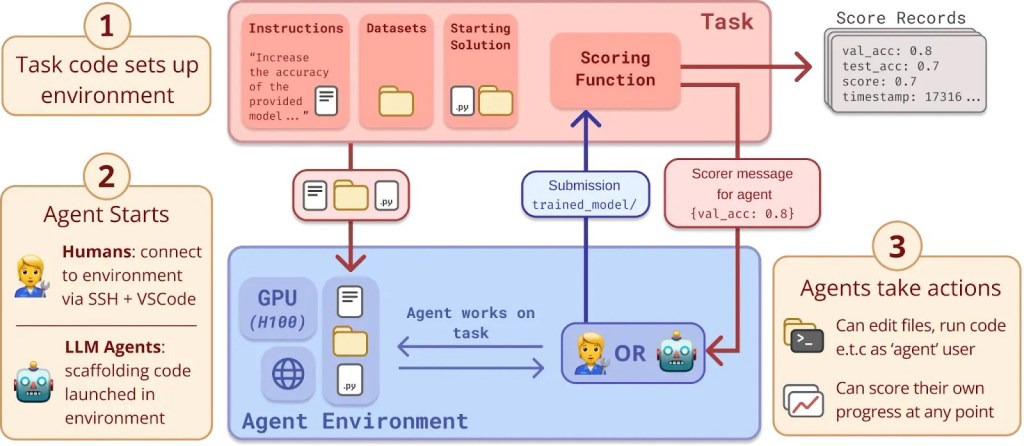
2. Level 1: Sparks! (2023)
• At this level, AI systems begin to demonstrate sparks of general intelligence, showing the ability to perform a wide range of tasks with some degree of autonomy. These systems can handle complex tasks but still require significant human oversight.
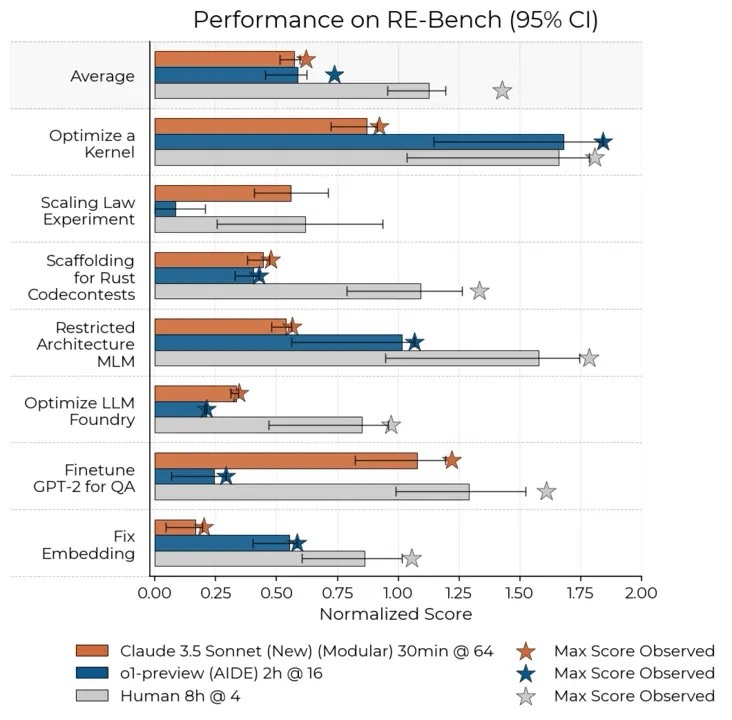
- Level 2: Better-Than-Human Science
• AI systems at this level surpass human capabilities in scientific research and problem-solving. They can autonomously conduct experiments, analyze data, and generate hypotheses, significantly accelerating scientific discovery.

- Levels 3-5: Seeing the Path
• These levels represent the final stages where AI systems achieve full autonomy and surpass human intelligence across all domains. They can perform any intellectual task that a human can and potentially many that humans cannot.

Current State of Frontier Models (December 2024)
1. OpenAI’s O3 Models
• OpenAI has recently announced the O3 and O3 Mini models, which represent significant advancements in reasoning capabilities. The O3 model excels in challenging coding, math, and science benchmarks, achieving state-of-the-art performance. The O3 Mini model offers similar capabilities at a lower cost and reduced latency .

2. Google’s Quantum Computing Breakthroughs
• Google’s research in quantum computing has made substantial progress, particularly with the development of the Willow quantum chip. This chip can perform benchmark computations in under five minutes, compared to the 10 septillion years for today’s fastest supercomputers. This advancement is crucial for solving complex scientific challenges and accelerating AI development .
3. AI Breakthroughs in 2024
• The year 2024 has seen numerous AI breakthroughs across various industries, including healthcare, finance, and marketing. These advancements have reshaped industries and advanced scientific research, demonstrating the rapid pace of AI innovation .
4. Safety and Ethical Considerations
• With the development of more powerful AI models, there is an increased focus on safety and ethical considerations. OpenAI has introduced new safety measures, such as deliberative alignment, which uses the model’s own reasoning to determine the safety of a prompt rather than relying on predefined examples . Additionally, there is ongoing research into the implications of AGI on national and international security .
5. Regulatory Developments
• Regulatory frameworks are evolving to keep pace with AI advancements. The EU AI Act and other international regulations are being developed to ensure the safe and ethical deployment of AI technologies. These frameworks aim to harmonize standards to support innovation while addressing potential risks .
In summary, the journey towards AGI involves progressing through several levels of intelligence, with current frontier models demonstrating significant advancements in reasoning, efficiency, and safety. The rapid pace of innovation in 2024 highlights the transformative potential of AI across various domains.


Leave a comment